
Gum disease is inflammation and infection of the tissues supporting and surrounding the teeth.
Gum disease also called Periodontal disease begins with bacterial growth in your mouth, red and inflamed gums, bleeding gums, pain, and if not treated leads to tooth loss(as the gums that support and surrounds the tooth gets damaged).
Gingivitis can occur at any age.
Poor oral hygiene:Improper teeth brushing, presence of Plaque and Calculus
Smoking: smoking damages gums tissue
Few medications resulting in dry mouth conditions(reduced salivary flow)
Hormonal changes:In pregnancy, menopause
Malocclusion:Brushing and oral hygiene maintenance becomes difficult in people having irregularly placed teeth
Illnesses such as in Diabetes, Cancer, HIV; blood disorders like leukemia, vitamin deficiency; Cardiovascular diseases
Studies have shown that Gingival health directly impacts your general health condition. Therefore, it is important to have a regular dental consultation every 6 months. The potential link between gum disease and other health problems is traced to the bacterial(bacteria in the mouth) invasion into the bloodstream, risking the immunity of medically compromised individuals. Gum disease is associated with health problems like stroke, heart problems, Diabetes and other Immuno compromised issues. The gum disease not only poses as a risk factor but also worsens the medical condition.
Gum diseases or Periodontal diseases are classified based on the severity of the infection into GINGIVITIS and PERIODONTITIS
Gingivitis is the Initial stage of gum disease.
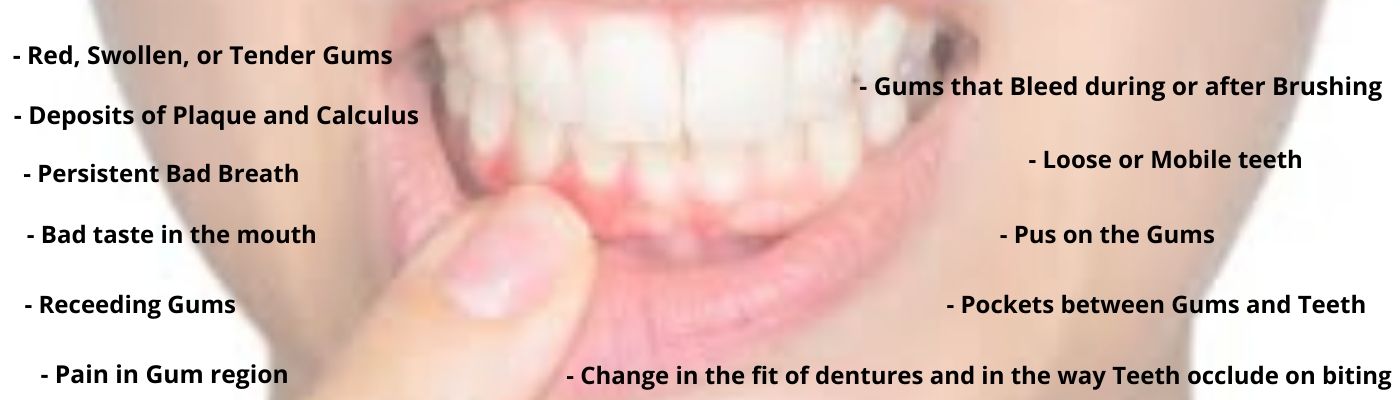
Gingivitis(Inflammation of the Gums) is a common infection that results due to the bacterial growth in gums. The Bacteria in the accumulated plaque and Calculus buildup causing the gums to become inflamed and bleed easily while brushing. The classic signs of Gingivitis are Red, swollen gums, tenderness in gums, bleeding gums on brushing.
Causes of Gingivitis are Poor oral hygiene, Malocclusion, few medical conditions etc.
Gingivitis, if not treated leads to periodontitis.
Gingivitis advanced to Periodontitis.
The Gingival infection pulls away the gums and bone away from tooth creating small spaces called POCKETS between the gums and tooth. These pockets harbor food debris, bacterial growth, and thus becomes infected. The severe infection damages the supporting structures of the teeth. The progressive loss of the supporting structures, gums and bone weakens the attachments to the tooth resulting in loose teeth, mobility of tooth. Periodontitis, if not treated results in tooth loss.

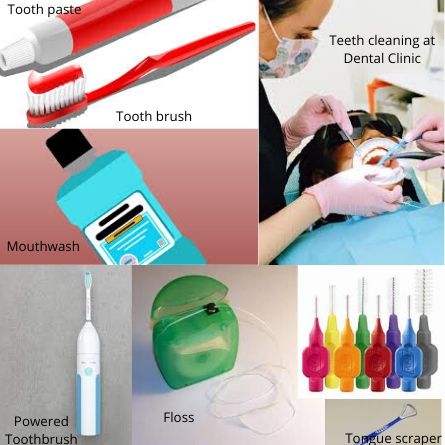
Gum diseases can be prevented by maintaining good Oral Hygiene. Maintenance of Good Oral Hygiene includes Professional teeth cleaning by the Dentist twice a year. Proper plaque control can be achieved by proper tooth brushing twice daily, use of a Fluoridated toothpaste, flossing to remove plaque in between the teeth and under the gum line and use of Anti-bacterial mouthwashes regularly.